Characteristics of Huperzine A Powder
2 min readHuperzine A (CAS No.: 102518-79-6) is an alkaloid derived from Chinese club moss (Huperzia serrata) and has been extensively studied for its cognitive enhancement and neuroprotective effects. In this blog post, SACH will share the characteristics of white crystalline huperzine a powder, including physical and chemical properties, chemical structure and stability, applications, etc.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Huperzine A Powder
Huperzine A is a white to light white crystalline powder with a molecular formula of C15H18N2O and a molecular weight of 242.3162. It has a density of approximately 1.6 g/cm³ and a melting point ranging from 211 to 216°C. Its boiling point is quite high, at around 479.5°C at 760 mmHg, and its flashpoint is 243.8°C. These properties make Huperzine A stable under normal storage conditions, provided it is kept sealed in a cool and dry environment, preferably at -20°C.
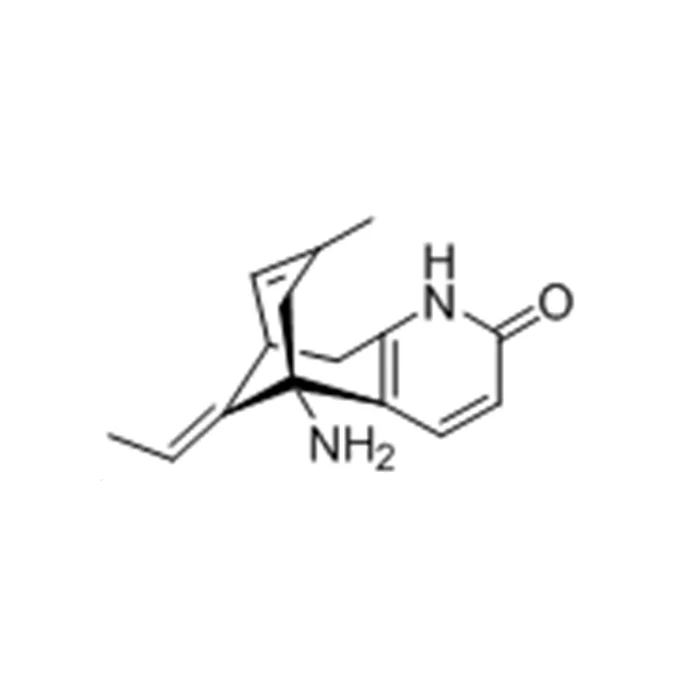
Chemical Structure and Stability of Huperzine A Powder
The chemical structure of Huperzine A is complex, featuring a unique arrangement of atoms that contribute to its pharmacological activity. Its stability is notable, as it does not decompose when stored and used according to recommended guidelines. This stability is crucial for maintaining its efficacy and safety, especially in pharmaceutical formulations where consistency is paramount.
Storage and Handling of Huperzine A Powder
Proper storage is essential for maintaining the integrity and efficacy of Huperzine A powder. It should be kept in a sealed container at -20°C to prevent degradation and ensure long-term stability. This storage condition is particularly important for laboratories and manufacturers that rely on the consistent quality of the compound for their research and production processes.
Applications of Huperzine A Powder
Huperzine A is primarily known for its role as an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. By selectively inhibiting AChE, it increases the levels of acetylcholine in the brain, a neurotransmitter essential for memory and learning. This mechanism of action makes Huperzine A particularly effective in treating memory disorders, including those associated with dementia and age-related cognitive decline.
Huperzine A can significantly improve memory recall, associative learning, and recognition abilities. It has also demonstrated efficacy in enhancing cognitive functions in patients with Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, and other neurodegenerative conditions. Its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier ensures that it reaches the central nervous system, where it can exert its therapeutic effects.

Conclusion
Huperzine A's unique chemical properties, stability and therapeutic applications make it a valuable asset for the treatment of memory impairment and cognitive decline. As research continues to unlock its full potential, Huperzine A will play an increasingly important role in improving cognitive health worldwide.
www.hzsqchem.com
SACH

